The Seasons of a Man’s Life: An Overview
If we think of stages, transitions, or sequences in adulthood at all, we tend to think less in terms of age than of singular events like moving away from home, getting married, starting one’s first job, having kids, and so on.
What Levinson discovered is that regardless of when these kinds of events happen along one’s chronological timeline, a more macro, universal order underlies them all. While the timing of life events, the overall content of life (family, career, lifestyle), and even the formation of a sense of maturity itself greatly differs between men, the sequence of seasons — the overall character of the life structure — remains the same for everyone. (As later studies showed, that includes women, for whom the basic architecture of the life cycle is largely similar, though some of the content and contours of the periods differ, befitting the unique experience of the female sex.) As Levinson puts it, just as everyone goes through identical developmental periods of childhood and adolescence, but have very different experiences of youth: “Individuals go through the periods [of adulthood] in infinitely varied ways, but the periods themselves are universal.”
(It is because the life cycle of adulthood runs independent from its discrete milestones (marriage, children, home ownership, etc.), that though the age which men achieve these traditional markers of maturity has gotten later, the overall structure of development that Levinson uncovered fifty years ago still holds up perfectly well.)
Just like the seasons of the year, the periods of adult development are neither good nor bad; rather, as each season is shaped by particular biological, psychological, and social factors, each simply brings “changes in the character of living.” In addition to having a qualitatively different mood and texture, each season has unique developmental tasks — choices and commitments that can either move a life forward and set up a healthy foundation for the next phase, or can create stagnation and crisis in the years to come.
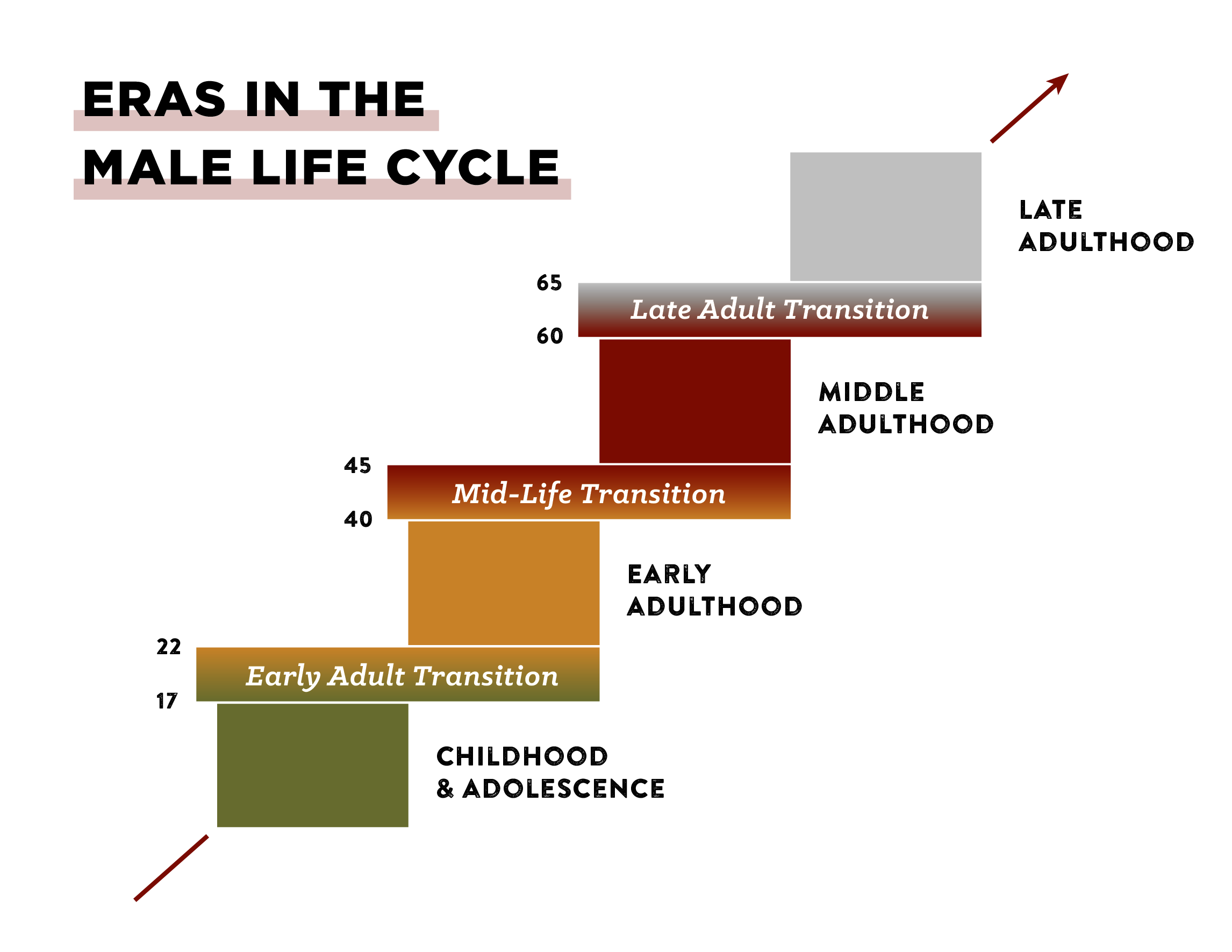
Diagram adapted from The Seasons of a Man’s Life
The broadest of these life phases are four eras that constitute the “skeletal structure of the life cycle”:
- Childhood and Adolescence: age 0-22
- Early Adulthood: age 17-45
- Middle Adulthood: age 40-65
- Late Adulthood: age 60-?
As you can see, the eras overlap with each other, e.g., Early Adulthood ends at age 45, while Middle Adulthood begins at age 40. These overlapping periods are called transitions. While the most significant and critical transitions of adult development come between eras — the Early Adult Transition, the Mid-Life Transition, and the Late Adult Transition — transitions also exist within these eras (the Age 30 and Age 50 Transitions).
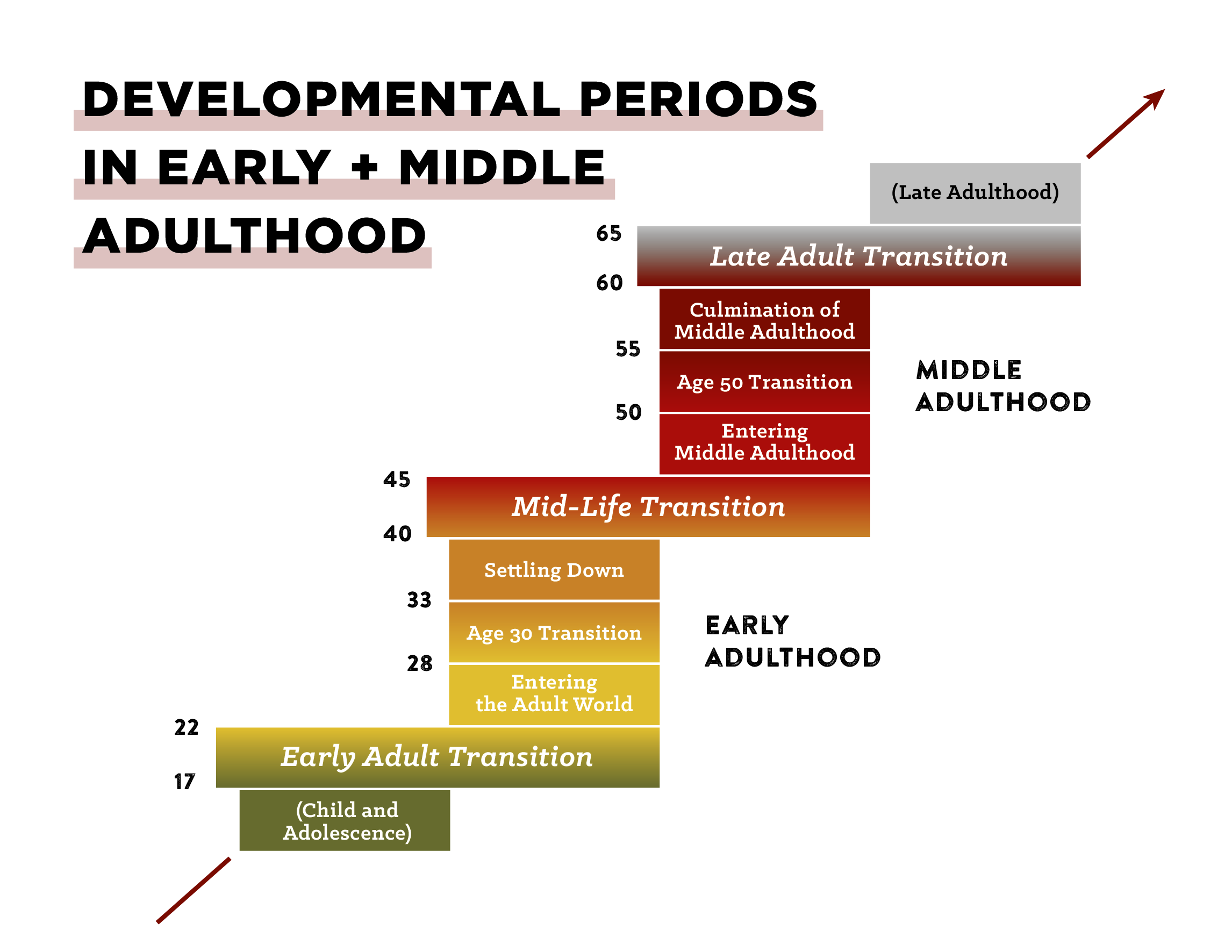
Diagram adapted from The Seasons of a Man’s Life
Every transitional, structure-changing period alternates with a more stable, structure-building period. Let’s take a closer look at the character of these different seasons:
Transitional/Structure-Changing Periods
Duration: ~4-5 years
Transitions serve as bridges that connect eras/periods in the life cycle. They terminate the past life structure and initiate a future life structure, but are themselves not wholly part of either. They are thus “zones of overlap,” liminal states; just as winter does not end abruptly, and suddenly become spring, transitions represent a time when one season of a man’s life is trending into the next.
Transitions are the “boundary zones between two states of greater stability,” during which an individual experiences his life as more malleable and makes changes to its structure.
During these periods, “a man must come to terms with the past and prepare for the future.”
He first looks back: how has he been doing in various areas like career, relationships, spirituality, and lifestyle? In what ways have goals been met or not met, and have particular values been lived out or ignored? Certain aspects of life inevitably feel stagnant and stuck in a rut, and a man must decide which parts of his past he wishes to keep, and which he wishes to discard. The process of letting go of certain relationships, pursuits, dreams, and expectations can evoke anger, grief, and a sense of loss.
At the same time that a man is bringing certain relationships and pursuits to an end, he begins to search about for alternative options, different possibilities, and new vistas for his life. Parts of the self that were neglected during the previous period, call out for attention. A sense of renewal, hope, and of making a fresh start is often present during a transition.
Each particular transition has its unique developmental tasks, but one they all share in common is the need to work to integrate what Levinson calls the Young/Old polarity. A man can be prematurely old, or try to maintain a predominance of youthfulness too long; each transition requires that he create a balance of these energies “appropriate to that time of life”:
Especially with the change in eras, there is normally an increase in the Old qualities of maturity, judgement, self-awareness, magnanimity, integrated structure, breadth of perspective. But these qualities are of value only if they continue to be vitalized by the Young’s energy, imagination, wonderment, capacity for foolishness and fancy. The Young/Old connection must be sustained.
Transitions can be subtle and smooth. Rather than looking to replace significant components in his life, a man may simply reaffirm or rejigger his commitment to existing ones. His job may not change, but his attitude towards it may. The structure of his family life may stay the same, but his perspective on it may shift. A relationship may remain extant, but on altered terms. He may deepen or detach his engagement with something he’s previously been more in limbo about. While it may not seem like a man’s life changes significantly during his kind of non-dramatic transition, by the end of it, his life structure is subtly different, and he feels different.
A smooth transition may be the result of a man entering these periods with a life structure that is already quite satisfactory. However, it also “may stem from resignation, inertia, passive acquiescence, or controlled despair.” That is, a man may feel stuck in his current circumstances and believing he cannot change, doesn’t change. In such cases, he will likely struggle in the phases to come.
On the other hand, transitions can also be times of crisis. A need for bigger, more significant changes is felt and wrestled with. A man may feel that he is unhappy in his marriage (or his bachelorhood), that he’s on the wrong career path, that he wants to make a geographic move, or that he needs to leave his faith. More dramatic pivots are contemplated.
Whether a transition is more quiet or chaotic, it “ends when the tasks of questioning and exploring have lost their urgency.” A man feels ready to move forward on the new or renewed commitments he has made (or resigned himself to). These choices “are the major product of the transition,” and the next step is to begin to build one’s life structure around them during the more stable period which ensues.
Stable/Structure-Building Periods
Duration: ~6-8 years
During a transition, an old life structure is terminated, and a new one is created. During the stable period which follows, a man then solidifies and enriches this new structure, lending it meaning and commitment, and pursing his goals and values within its architecture.
Stable periods are not wholly tranquil, nor free from stress, difficulties, and change — the process of building and strengthening one’s life structure, as well as the basic nature of life itself, is invariably full of challenges — but they are more steady, straightforward, and settled than transitional periods.
In addition to the underlying task of enhancing one’s life structure, each particular stable period has its own set of unique developmental tasks.
While the tasks of both stable and transitional periods are universal to everyone, each man will go about his work on them in very diverse, very individual ways, and the tasks can be done either well or poorly; though as Levinson notes, making such judgements is difficult since ideas of success are subjective and idiosyncratic. In this context, “success” is a matter of whether or not the developmental tasks of a particular period are engaged, and whether or not the changes and commitments that come out of this engagement are satisfactory to the self and viable given one’s circumstances.
A key takeaway in examining the overall structure of the adult life cycle, is that getting older, rather than being a process of creating a permanent, concrete stability — a monolithic structure that lasts for three-quarters of a century — is instead an oscillation of creation and re-creation, destruction and renewal, ideally with an upwards, generative arc.
In this series, we’ll take a closer look at the particular periods within this trajectory. While Levinson’s study made some speculative hypotheses about the nature of the life cycle after midlife, its research largely focused on the periods from the late teens up through about age 45. So that is the range we will concentrate on, first covering the era of Early Adulthood, and then devoting a separate piece to the Mid-Life Transition.
0 Comments